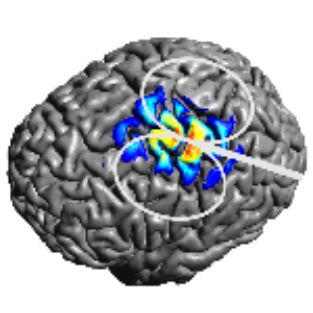
TDCS Optimization¶
SimNIBS can automatically optimize TDCS montages for maximal focality or intensity at the target. There are two steps for performing the optimizations.
Create a leadfield.
Set-up an optimization based on the leadfield.
Note
When using this feature in a publication, please cite Saturnino, G. B., Siebner, H. R., Thielscher, A., & Madsen, K. H. (2019). Accessibility of cortical regions to focal TES: Dependence on spatial position, safety, and practical constraints. NeuroImage, 203, 116183.
Leadfield Calculations¶
The leadfield is calculated by first placing many electrodes on the head, for example according to an EEG cap, and afterwards calculating the field caused by each electrode individually, keeping a constant return electrode.
With this simulations, we form a matrix which can then be used to calculate the electric field caused by any combination of electrodes. As the leadfield involves calculating many electric fields, it takes some time to run, but usually no more than one hour.
To calculate leadfields, the user must write a small Python or Matlab script using the TDCSLEADFIELD structure. Unless specified differently, the leadfields are calculated for EEG 10-10 electrode positions.
Python
''' Example of a SimNIBS tDCS leadfield in Python Run with: simnibs_python leadfield.py Copyright (C) 2019 Guilherme B Saturnino place script in the main folder of the example dataset ''' from simnibs import sim_struct, run_simnibs tdcs_lf = sim_struct.TDCSLEADFIELD() # subject folder tdcs_lf.subpath = 'm2m_ernie' # output directory tdcs_lf.pathfem = 'leadfield' # Uncoment to use the pardiso solver #tdcs_lf.solver_options = 'pardiso' # This solver is faster than the default. However, it requires much more # memory (~12 GB) run_simnibs(tdcs_lf)
MATLAB
% Example of a SimNIBS tDCS leadfield % Copyright (C) 2019 Guilherme B Saturnino % place script in the main folder of the example dataset tdcs_lf = sim_struct('TDCSLEADFIELD'); % subject folder tdcs_lf.subpath = 'm2m_ernie'; % Output directory tdcs_lf.pathfem = 'leadfield'; % Uncomment to use the pardiso solver %tdcs_lf.solver_options = 'pardiso'; % This solver is much faster than the default. However, it requires much more % memory (~12 GB) run_simnibs(tdcs_lf)
Here, we are calculating a leadfield in the ernie example data set based on the EEG 10-10 system.
Note
For more options in running tDCS leadfields, please see the documentation TDCSLEADFIELD.
This script will create the files in the leadfield folder:
ernie_electrodes_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.msh: File with the head mesh and electrodes placed on top. Can be used for checking electrode positions. Be aware that some electrodes will have the same color as the skin.ernie_ROI.msh: The region of interest where the electric field values were recorded. In the example, the middle gray matter surface.ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5: HDF5 file with the leadfield matrix, organized with the datasets:mesh_electrodes: Full mesh with the electrodesmesh_leadfield: Mesh with the region of interest only (in the example, the middle gray matter surface). Contains themesh_leadfield/leadfields/tdcs_leadfielddata set with the leadfield. In the attributes, you can see information such as the reference electrode, the field (E or J), units, currents and so on.
Note
Meshes stored in HDF5 files can be read with the
simnibs.msh.Msh.read_hdf5()class or with the mesh_load_hdf5 function in MATLAB.
Optimization¶
Now, we will use the leadfield to optimize the electric field at a given target.
Simple Optimization¶
The first step is to set the TDCSoptimize structure. In this structure, we need to select the leadfield we will use for the optimization, a name for the optimization problem, safety constraints and limit the number of electrodes.
Afterwards, we define an optimization target using a TDCStarget structure.
Python
''' Example of a SimNIBS tDCS optimization in Python Run with: simnibs_python tdcs_optimize.py Copyright (C) 2019 Guilherme B Saturnino ''' import simnibs # Initialize structure opt = simnibs.opt_struct.TDCSoptimize() # Select the leadfield file opt.leadfield_hdf = 'leadfield/ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5' # Select a name for the optimization opt.name = 'optimization/single_target' # Select a maximum total current (in A) opt.max_total_current = 2e-3 # Select a maximum current at each electrodes (in A) opt.max_individual_current = 1e-3 # Select a maximum number of active electrodes (optional) opt.max_active_electrodes = 8 # Define optimization target target = opt.add_target() # Position of target, in subject space! # please see tdcs_optimize_mni.py for how to use MNI coordinates target.positions = [-50.7, 5.1, 55.5] # Intensity of the electric field (in V/m) target.intensity = 0.2 # Run optimization simnibs.run_simnibs(opt)
MATLAB
% Example of a SimNIBS tDCS optimization in MATLAB % % Copyright (C) 2019 Guilherme B Saturnino % Initialize structure opt = opt_struct('TDCSoptimize'); % Select the leadfield file opt.leadfield_hdf = 'leadfield/ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5'; % Select a name for the optimization opt.name = 'optimization/single_target'; % Select a maximum total current (in A) opt.max_total_current = 2e-3; % Select a maximum current at each electrodes (in A) opt.max_individual_current = 1e-3; % Select a maximum number of active electrodes (optional) opt.max_active_electrodes = 8; % Define optimization target % Position of target, in subject space! % please see tdcs_optimize_mni.m for how to use MNI coordinates opt.target.positions = [-50.7, 5.1, 55.5]; % Intensity of the electric field (in V/m) opt.target.intensity = 0.2; % Run optimization run_simnibs(opt);
Note
For more information see the documentation for TDCSoptimize and TDCStarget.
Output files¶
The optimization outputs:
name.csv: comma separated values (CSV) files with optimal current values at each electrode (in A)name_electrodes.geo: Gmsh .geo file for visualizing electrodes and currentsname.msh: Gmsh .msh file with the target and the optimized electric field in the ROIname_summary.txt: Some summary quantities about the optimization
Maximizing intensity¶
To maximize intensity at the target, disregarding field focality, simply use a large value for the target intensity.
Python
''' Example of optimizaion maximizing intensity in the target Copyright (C) 2019 Guilherme B Saturnino ''' import simnibs opt = simnibs.opt_struct.TDCSoptimize() opt.leadfield_hdf = 'leadfield/ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5' opt.name = 'optimization/single_target' opt.max_total_current = 2e-3 opt.max_individual_current = 1e-3 opt.max_active_electrodes = 8 target = opt.add_target() target.positions = [-50.7, 5.1, 55.5] # Set the intensity to a large value (e.g, 100) target.intensity = 100 # Run optimization simnibs.run_simnibs(opt)
MATLAB
% Example of optimization maximizing intensity in the target % % Copyright (C) 2019 Guilherme B Saturnino opt = opt_struct('TDCSoptimize'); opt.leadfield_hdf = 'leadfield/ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5'; opt.name = 'optimization/single_target'; opt.max_total_current = 2e-3; opt.max_individual_current = 1e-3; opt.max_active_electrodes = 8; opt.target.positions = [-50.7, 5.1, 55.5]; % Set the intensity to a large value (e.g, 100) opt.target.intensity = 100; % Run optimization run_simnibs(opt);
Using MNI Coordinates¶
The target positions are, as always in SimNIBS, given in world coordinates in subject space (see here for more information). However, we can use the mni2subject_coords function to transform coordinates from MNI space to subject space. When the transformed coordinates are outside the gray matter of the subject, they will be projected onto the closest gray matter position.
Python
import simnibs opt = simnibs.opt_struct.TDCSoptimize() opt.leadfield_hdf = 'leadfield/ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5' opt.name = 'optimization/MNI_target' opt.max_total_current = 2e-3 opt.max_individual_current = 1e-3 opt.max_active_electrodes = 8 target = opt.add_target() # Transfrorm a set of coordinates from MNI space to subject space. # The second argument of the mni2subject_coords function # is the path to the "m2m_subID" folder. target.positions = simnibs.mni2subject_coords([-37, -21, 58], 'm2m_ernie') target.intensity = 0.2 # Run optimization simnibs.run_simnibs(opt)
MATLAB
opt = opt_struct('TDCSoptimize'); opt.leadfield_hdf = 'leadfield/ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5'; opt.name = 'optimization/MNI_target'; opt.max_total_current = 2e-3; opt.max_individual_current = 1e-3; opt.max_active_electrodes = 8; % Transfrorm a set of coordinates from MNI space to subject space. % The second argument of the mni2subject_coords function % is the path to the "m2m_subID" folder. opt.target.positions = mni2subject_coords([-37, -21, 58], 'm2m_ernie'); opt.target.intensity = 0.2; % Run optimization run_simnibs(opt);
Multiple targets¶
To optimize multiple distant targets simultaneously, just use multiple target structures.
Python
''' Example of an optimization with two targets ''' import simnibs opt = simnibs.opt_struct.TDCSoptimize() opt.leadfield_hdf = 'leadfield/ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5' opt.name = 'optimization/two_targets' opt.max_total_current = 4e-3 opt.max_individual_current = 2e-3 opt.max_active_electrodes = 8 # Target in the left motor cortex target_left = opt.add_target() target_left.positions = [-30.3, 5.4, 71.6] target_left.intensity = 0.2 # Target in the right motor cortex target_right = opt.add_target() target_right.positions = [36.0, 2.5, 72.6] target_right.intensity = -0.2 # negative value reverses direction simnibs.run_simnibs(opt)
MATLAB
% Example of an optimization with two targets % opt = opt_struct('TDCSoptimize'); opt.leadfield_hdf = 'leadfield/ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5'; opt.name = 'optimization/two_targets'; opt.max_total_current = 4e-3; opt.max_individual_current = 2e-3; opt.max_active_electrodes = 8; % Target in the left motor cortex opt.target(1).positions = [-30.3, 5.4, 71.6]; opt.target(1).intensity = 0.2; % Target in the right motor cortex opt.target(2).positions = [36.0, 2.5, 72.6]; opt.target(2).intensity = -0.2; run_simnibs(opt);
By using multiple targets, SimNIBS will try to hit each target with its respective intensity. When setting many positions in a single target, SimNIBS will try to hit the average intensity over the multiple positions.
Electric Field Strength¶
For using electric field strength (magnitude) rather than a specific direction, just set the directions attribute to None (Python) or ‘none’ (MATLAB). This feature has been introduced in SimNIBS 3.2 and uses a novel optimization method.
Python
''' Optimize controlling electric field strength ''' import simnibs opt = simnibs.opt_struct.TDCSoptimize() opt.leadfield_hdf = 'leadfield/ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5' opt.name = 'optimization/strength' opt.max_total_current = 4e-3 opt.max_individual_current = 2e-3 opt.max_active_electrodes = 8 # Target in the left motor cortex target_left = opt.add_target() target_left.positions = [-30.3, 5.4, 71.6] target_left.intensity = 0.2 target_left.directions = None # Target in the right motor cortex target_right = opt.add_target() target_right.positions = [36.0, 2.5, 72.6] target_right.intensity = 0.2 target_right.directions = None simnibs.run_simnibs(opt)
MATLAB
% Optimize controlling electric field strength % opt = opt_struct('TDCSoptimize'); opt.leadfield_hdf = 'leadfield/ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5'; opt.name = 'optimization/strength'; opt.max_total_current = 4e-3; opt.max_individual_current = 2e-3; opt.max_active_electrodes = 8; % Target in the left motor cortex opt.target(1).positions = [-30.3, 5.4, 71.6]; opt.target(1).intensity = 0.2; opt.target(1).directions='none'; % Target in the right motor cortex opt.target(2).positions = [36.0, 2.5, 72.6]; opt.target(2).intensity = 0.2; opt.target(2).directions='none'; run_simnibs(opt);
Note
When using this feature in a publication, please cite Saturnino, G. B., Madsen, K. H., & Thielscher, A. (2020). Optimizing the Electric Field Strength in Multiple Targets for Multichannel Transcranial Electric Stimulation. bioRxiv.
Avoidance Regions¶
You can also add regions where the electric field should be more penalized than elsewhere. This is done using the avoid optional structure. In this examples, we will set the field to avoid the eyes.
Python
''' Example of an optimization punishing more the field in the eyes Copyright (C) 2019 Guilherme B Saturnino ''' import simnibs opt = simnibs.opt_struct.TDCSoptimize() opt.leadfield_hdf = 'leadfield/ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5' opt.name = 'optimization/avoid' opt.max_total_current = 2e-3 opt.max_individual_current = 1e-3 opt.max_active_electrodes = 8 target = opt.add_target() target.positions = simnibs.mni2subject_coords([-37, -21, 58], 'm2m_ernie') target.intensity = 0.2 avoid = opt.add_avoid() avoid.tissues = 1006 # 1006 corresponds to the eye surface # Run optimization simnibs.run_simnibs(opt)
MATLAB
% Example of an optimization punishing more the field in the eyes % % Copyright (C) 2019 Guilherme B Saturnino opt = opt_struct('TDCSoptimize'); opt.leadfield_hdf = 'leadfield/ernie_leadfield_EEG10-10_UI_Jurak_2007.hdf5'; opt.name = 'optimization/avoid'; opt.max_total_current = 2e-3; opt.max_individual_current = 1e-3; opt.max_active_electrodes = 8; opt.target.positions = mni2subject_coords([-37, -21, 58], 'm2m_ernie'); opt.target.intensity = 0.2; opt.avoid.tissues = 1006; % 1006 corresponds to the eye surface % Run optimization run_simnibs(opt)
Note
For more options and information on avoidance regions please see the reference for the TDCSavoid structure. You can visualize the position of the avoided region in the results by deselecting magnE in gmsh, and selecting avoid_1.